复制数组
复制数组-循环
1 | var arr=[1,2,3]; |
复制数组-Array.from(arr)
1 | var arr=[1,2,3]; |
复制数组-var arr2=[…arr]; (… 超引用)
1 | var arr=[1,2,3]; |
赋值数组-…示例 (… 超引用)
1 | function show(){ |
1 | function show(...args){ |
循环
for in (可以循环数组,json)
1 | var arr=['apple','banana','orange','pear']; |
1 | var json={'a':'apple','b':'banan','c':'pear','d':'orange'}; |
for of (可以循环数组,不能循环json)
1 | var arr=['apple','banana','orange','pear']; |
1 | var json={'a':'apple','b':'banan','c':'pear','d':'orange'}; |
Map对象
Map对象和json相似,也是一种key-value形式.Map对象为了和for of循环配合而生的.
new Map();
1 | var map=new Map(); |
遍历map (不能使用for in,没有效果)
1 | var map=new Map(); |
for… of也可以循环数组
1 | 只循环值: |
箭头函数
1 | 原来写法 箭头函数 => |
箭头函数-应用
1 |
|
箭头函数-注意
this问题,this指向了window.
arguments,不能使用了.
1 |
|
1 |
|
对象
对象语法简洁化
单体模式
面向对象
之前类的写法
1 | function Person(name,age){ //类、构造函数 |
ES6写法
1 | //构造函数 constructor 生成完实例以后,自己就执行的 |
面向对象-函数给默认值
1 | function move(obj='对象必须要填写的',json={},options){ |
面向对象-继承
1 | // 之前写法: 子类.prototype=new 父类(); |
1 | //ES6写法: |
面向对象-队列类
1 | class Queue{ |
1 | class Queue{ |
1 |
|
模块化(ES6自带模块化)
如何定义(导出)模块
a.js1
2const a=12;
export default a;
b.js1
2const a=5;
export default a;
导出多个模块1
2
3const a=5;
const b=12;
export default {a,b};
如何使用(引用))
demo.js1
2
3import modA from './a.js';
import modB from './b.js';
console.log(modA+modB); // 17
Promise -> 承诺
就是一个对象,用来传递异步操作的数据(消息).
pending(等待、处理中) ―> Resolve(完成、fullFilled) ―> Rejected(拒绝、失败).
初识 Promise()
1 | var p1 = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) { |
Promise() 可以连续返回结果
1 |
|
Promise 异步数据的传递
promise.js1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15const fs=require('fs');
fs.readFile('let.html',function(err,data){
var p1=new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
if(err){
reject(err);
}else{
resolve(data);
}
});
p1.then(function(value){
console.log(value.toString());
},function(value){
console.log(value);
});
});
终端输入命令,如果读取到了数据:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25leo@lenovo MINGW64 /e/BaiduNetdiskDownload/ES6/ES6课件
$ node promise.js
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>智能社——http://www.zhinengshe.com</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximu
m-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0">
<meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes">
<meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-status-bar-style" content="black">
<style>
</style>
<script src="traceur.js"></script>
<script src="bootstrap.js"></script>
<script type="module">
let a=12;
alert(a);
console.log(a);
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
终端输入命令,没有读取到数据:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8leo@lenovo MINGW64 /e/BaiduNetdiskDownload/ES6/ES6课件
$ node promise2.js
{ Error: ENOENT: no such file or directory, open 'E:\BaiduNetdiskDownload\ES6\ES6课件\let123.html'
at Error (native)
errno: -4058,
code: 'ENOENT',
syscall: 'open',
path: 'E:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\ES6\\ES6课件\\let123.html' }
Promise.catch ――> 用来捕获错误
1 | var p1=new Promise(function(resolve,reject){ |
输出结果:1
2成功了
发生错误了
Promise.all
全部,用于将多个promise对象,组合,包装成一个全新的promise实例
Promise.all([p1,p2,p3…]);
所有的promise对象,都正确,才走成功
否则,只要有一个错误,是失败了
1 | var p1=Promise.resolve(3); |
1 | var p1=Promise.resolve(3); |
Promise.race
返回也是一个promise对象
最先能执行的promise结果,哪个最快,用哪个1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10var p1=new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
setTimeout(resolve,50,'one');
});
var p2=new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
setTimeout(resolve,100,'two');
});
Promise.race([p1,p2]).then(function(value){
console.log(value);
});
// 输出: one
Generrator -> 生成器
是一个函数,可以遍历,Generrator就是一个状态机.
语法:
function show(){ //普通函数
}
function* show(){ //generator函数
yield xxx
}
形式上:
a). 函数名字前面有 *
b). 函数内部使用 yield语句
function* show(){
yield 'Hello';
yield 'World';
yield 'Es6';
}
var res=show();
res.next() {value:'Hello', done:false}
res.next() {value:'World', done:false}
res.next() {value:'Es6', done:false}
res.next() {value:'undefined', done:true}
总结: 每次返回一个value和done结果
value,每次yield后面值
done是一个布尔值,代表是否遍历结束
yield是否有返回值?
yield语句本身没有返回值,或者每次返回undefined
next可以带参数?
给上一个yield值
for....of循环: 循环generator函数
generator函数放到对象里面:
var json={
*show(){
yield 'xx';
yield 'xx';
}
}
Generrator -> demo1
1 |
|
输出结果: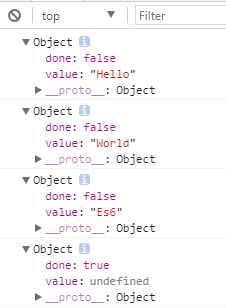
Generrator -> demo2
1 | function* show(){ |
Generrator -> yield 是否有返回值
yield语句本身没有返回值, 或者每次返回undefined1
2
3
4
5
6
7function* show(){
var a=yield 'Hello';
return a;
}
var res=show();
console.log(res.next()); // {value:'Hello', done:false}
console.log(res.next()); // {value:'undefined', done:true}

